Have you ever wondered why we have day and night? Or why the Sun seems to rise in the east and set in the west?
All of this happens because of Earth’s rotation. It’s one of the most fascinating natural movements that keeps our planet in balance. In this article, we’ll explore what Earth rotation is, how it works, why it’s important, and how it affects life on our planet.
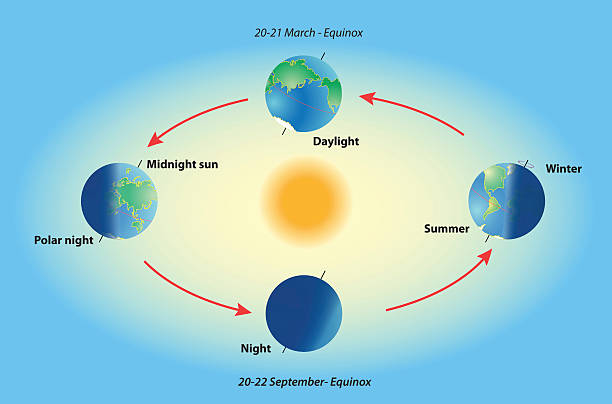
What Is Earth Rotation?
Earth rotation means the spinning of our planet around its own axis.
The Earth completes one full rotation every 24 hours, which gives us day and night.
-
The axis is an imaginary line running through the North and South Poles.
-
Earth rotates from west to east, which makes the Sun appear to rise in the east and set in the west.
So, while it feels like the Sun moves across the sky, it’s actually the Earth that’s spinning!
Duration of Earth’s Rotation
-
One sidereal day (rotation relative to distant stars) = 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds.
-
One solar day (rotation relative to the Sun) = 24 hours.
The small difference occurs because Earth is also orbiting around the Sun while spinning.
Why Does the Earth Rotate?
When the Solar System was forming billions of years ago, clouds of gas and dust began to spin. As these particles came together to form planets, they continued rotating due to the law of conservation of angular momentum.
That’s why all planets, including Earth, still spin today.
Effects of Earth’s Rotation
Earth’s rotation affects our planet in many ways. Let’s look at the main effects:
-
Day and Night:
The rotation causes different parts of Earth to face the Sun at different times, resulting in day and night. -
Time Zones:
Since Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, it turns 15° every hour — giving us 24 time zones across the world. -
Coriolis Effect:
This effect causes moving air and water to deflect, influencing wind patterns and ocean currents. -
Shape of the Earth:
Due to its rotation, Earth is not a perfect sphere — it bulges at the equator and flattens at the poles. -
Tides and Ocean Currents:
Combined with the Moon’s gravity, rotation helps in the regular rise and fall of ocean tides. -
Variation in Gravity:
Gravity is slightly weaker at the equator than at the poles due to centrifugal force from rotation.
Interesting Facts About Earth’s Rotation
-
The Earth spins at about 1,670 km/hour (around 465 m/s) at the equator.
-
The rotation is gradually slowing down — very slightly — due to gravitational forces from the Moon.
-
Millions of years ago, a day was only about 22 hours long!
-
Every 100 years, the length of a day increases by roughly 1.7 milliseconds.
-
Shifts in mass (like melting ice or groundwater movement) can slightly change Earth’s rotation speed and axis position.
20 Important MCQs on Earth Rotation :
#1. Earth rotates about how many degrees per hour?
#2. The Earth rotates once in:
#3. How long does it take Earth to rotate 360°?
#4. Earth rotates from:
#5. Which phenomenon is not caused by rotation?
#6. A sidereal day is approximately:
#7. Which of the following statements is true?
#8. Which natural event proves Earth’s rotation?
#9. Which force causes deflection of winds due to Earth’s rotation?
#10. The imaginary line around which the Earth rotates is called:
#11. What is responsible for the bulging of Earth at the equator?
#12. Earth’s axis is tilted by approximately:
#13. What happens due to rotation at the equator?
#14. The rotation of the Earth causes:
#15. The axis of Earth is an imaginary line that passes through:
#16. Earth’s rotation speed is maximum at:
#17. The Earth’s axis passes through:
#18. The time taken by Earth to complete one rotation is:
#19. Which of the following causes day and night?
#20. The shape of the Earth is:
Results
You Passed
Try Again
You can also read this:
Solar System Quiz with Answers
FAQs About Earth Rotation
Q1: What is meant by Earth’s rotation?
A: It is the spinning of Earth around its own axis, causing day and night.
Q2: In which direction does Earth rotate?
A: From west to east.
Q3: What is the difference between a solar day and a sidereal day?
A: A solar day (24 hours) is based on the Sun’s position; a sidereal day (23 hours 56 minutes) is based on distant stars.
Q4: What causes day and night?
A: The rotation of Earth on its axis.
Q5: Can Earth’s rotation stop?
A: No, but it is slowly decreasing due to the Moon’s tidal friction.



